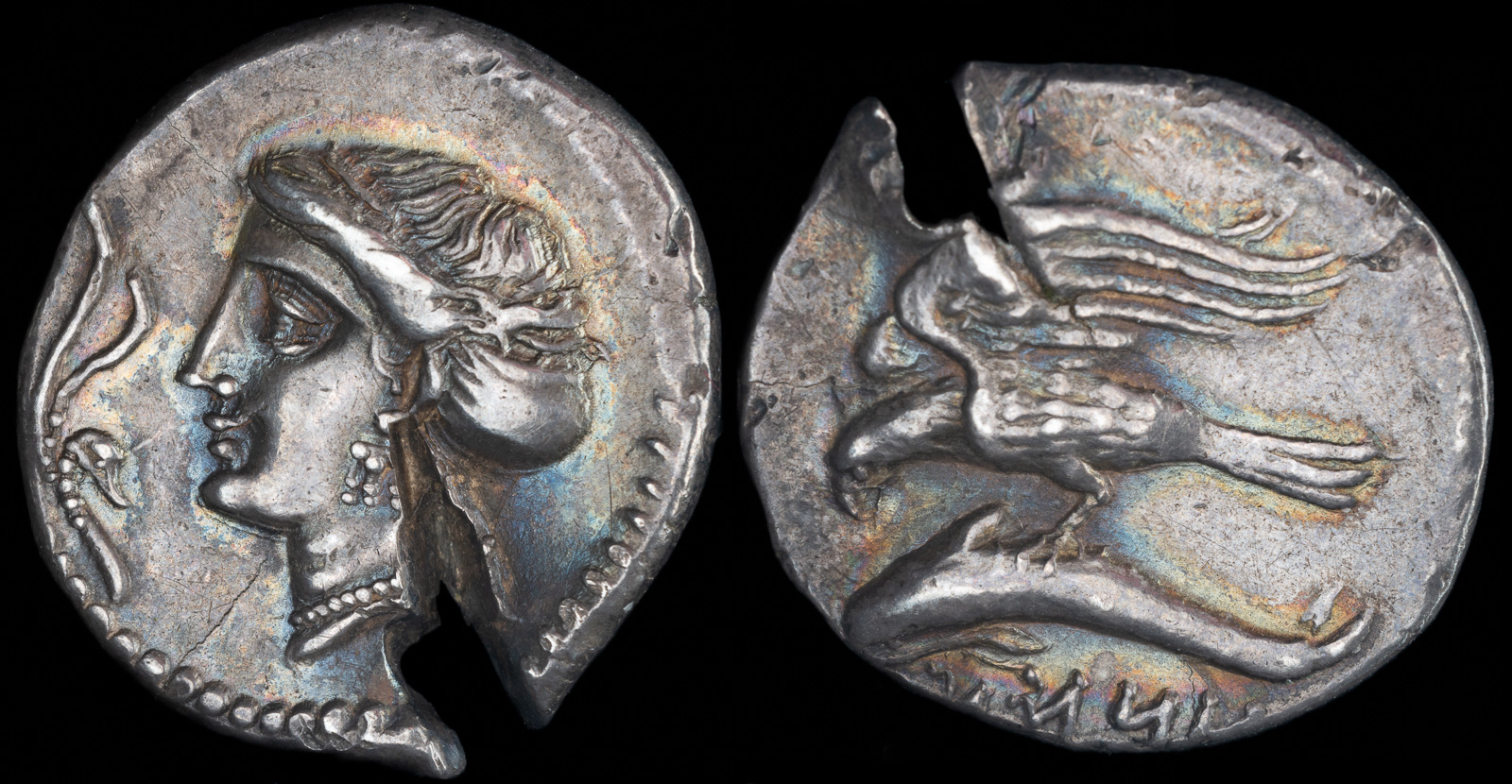
Eagle
View All Tags
In ancient Greece, the eagle was primarily associated with Zeus, the king of the gods. As a symbol of Zeus’s power and sovereignty, the eagle was often depicted as his sacred bird, serving as both his companion and messenger. In many myths, Zeus would transform into an eagle or send an eagle to carry out tasks on his behalf. The eagle’s powerful presence symbolized Zeus’s dominion over the heavens and his authority over both gods and humans. The bird’s ability to soar to great heights and its sharp vision made it a fitting representation of Zeus’s all-seeing nature and his supreme control over the cosmos. The eagle also had associations with victory and strength, qualities that were central to Zeus’s role as a god of justice and ruler of the gods.
In the context of Roman culture, the eagle became an even more prominent symbol, particularly in the military. The Roman eagle (aquila) was adopted as the standard for the Roman legions, symbolizing the power and unity of the Roman Empire. The aquila was a sacred symbol, carried into battle by Roman soldiers, and its loss or capture was seen as a great dishonor. The eagle was also connected to Jupiter, the Roman counterpart to Zeus, and was used to represent the god’s divine authority and rule over the empire. Roman emperors, like their Greek counterparts, were often depicted with eagles as symbols of their divine favor and imperial power. The eagle’s association with Jupiter elevated it as a symbol of Roman strength, divine protection, and military prowess.
The eagle’s symbolism of imperial power was especially evident in the iconography of Roman coins, where the eagle frequently appeared as a prominent motif. It was often shown perched on a globe, representing the emperor’s dominion over the world, or in flight, emphasizing the reach and superiority of the Roman Empire. In this context, the eagle not only symbolized military might but also the divine sanction of the emperor’s rule. As the eagle was associated with the gods, its image on coins and standards served to remind the Roman people of their connection to the divine and the emperor’s role as the earthly representative of that divine power.

Abdasan, 360-330 BCE

Abydos, Troas 4th-3rd cent BCE

Adramytteion, Mysia 350 BCE

Aeolis, Kyme 350-250 BCE

Aizanis, Phrygia 41-54 CE

Alexander I Molossos 334-331 BCE

Alexander I Molossos 334-332 BCE

Alexander III 325-323 BCE

Alexander III 336-323 BCE

Alexander IV/Antipater 323-317 BCE

Alexander the Great 330-323 BCE

Alexandria Eschate 285-280 BCE

Amyntas III 393-369 BCE

Andragoras 246-238 BCE

Androkles of Amathos 325-323 BCE

Antigenes 322-320 BCE

Antigonos Monophthalmos 305-300 BCE

Aphytis, Macedon 430-390 BCE

Archon or Dokimos 323-317 BCE

Ariarathes I 325 BCE

Ariassos, Pisidia 1st Century BCE

Aspesias 316-311 BCE

Berenikie II 244-221 BCE

Blaundos, Lydia 200-100 BCE

Cadi, Phrygia 41-54 CE

Carus 282-283 CE

Chalkis, Euboia 290-271 BCE

Charaspes 190-188 BCE

Cyrrhus, Cyrrhestica 247-249 CE

Deiotaros 62-40 BCE

Dia, Bithynia 85-65 BCE

Diodotos I of Baktria 255-235 BCE

Elis, Olympia 111th Olympiad 336 BCE

Emerita, Hispania 27 BCE-14 CE

Euhippe, Caria 300 BCE

Gortyna, Crete 250-221 BCE

Grimenothyrae, Phrygia

Halikarnassos 4th-3rd Centuries BCE

Hierapolis-Kastabala, Kilikia 2nd-1st centuries BCE

Hiketas II, Syracuse 287-278 BCE

Istros, Moesia 350-250 BCE

Italica, Iberia 14-37 CE

Itanos, Crete 320-280 BCE

Juliopolis, Bithynia 253-268 CE

Kalas/Demarchos 325-323 BCE

Kentoripai, Sicily 344-336 BCE

Koinon of Macedon 222-235 CE

Koinos 324/323 BCE

Kotys IV 171-167 BCE

Kyme, Aeolis 320-250 BCE

Kyme, Aeolis 320-250 BCE

Lakedaimon (Sparta) 226-223 BCE

Lakedaimon (Sparta) ca 48-35 BCE

Licinius II 321-324 CE

Lyttos, Crete 3rd century BCE

Mazaios 361-334 BCE

Megara, Megaris 198-217 CE

Memphis, Egypt 323/2 BCE

Menelaus 315-306 BCE

Nikokles of Paphos 325-317 BCE

Nikomedes II 110/9 BCE

Nikomedes III 126/5 BCE

Okokleia, Phrygia 238-244 CE

Olosson, Thessaly 400-350 BCE

Orra, Calabria 250-225 BCE

Perdikkas 321/320 BCE

Perseus 179-168 BCE

Pharnakeia, Pontos 85-65 BCE

Philip III Arrhidaeos 331-321 BCE

Philotas 400-380 BCE

Philoxenos 325-323 BCE

Phintias, Akragas, Sicily 287-279 BCE

Praisos, Crete 300-270 BCE

Ptolemaios 85-40 BCE

Ptolemy Epigonos 246-221 BCE

Ptolemy I Soter 311-305 BCE

Ptolemy II Philadelphos 256/55 BCE

Ptolemy IV 222-204 BCE

Ptolemy Keraunos 281-279 BCE

Ptolemy Keraunos 281-279 BCE

Ptolemy V 205-180 BCE

Pydna, Macedonia 381-369 BCE

Seuthes III 323-316 BCE

Siphnos, Cyclades 4th century BCE

Stamenes/Archon 324/323 BCE

Syennesis 440-400 BCE

Tarsos, Cilicia 150 BCE
Tavium, Galatia 59-50 BCE

Thyateira, Lydia 193-235 CE

Tigranes II 80-68 BCE

Tios, Bithynia 300 BCE

Tomis, Moesia 209-211 CE

Trajan 115 CE
