Athena
View All Tags
As the goddess of wisdom, Athena played a central role in the intellectual and moral life of the Greeks. She was seen as the embodiment of rational thought, knowledge, and skill. Her wisdom was not only academic but also practical, often guiding heroes and leaders in their decisions. Athena’s ability to provide strategic counsel and support made her an important deity for generals and warriors, and she was frequently depicted as aiding heroes such as Odysseus and Perseus. Her wisdom extended beyond military matters; she was also associated with craftsmanship, particularly weaving and pottery, reflecting the importance of creative skills in ancient Greek society.
Athena was also the goddess of warfare, but her approach to combat was distinct from that of Ares, the god of violent and chaotic war. Athena represented strategic warfare, emphasizing intelligence, planning, and discipline over brute force. She was a protector of the state and city, and her role was often to ensure victory through clever tactics and careful preparation. Unlike Ares, who symbolized the destructive and chaotic aspects of war, Athena embodied the nobility and honor of battle, often leading warriors to victory with wisdom rather than sheer violence. This aspect of her nature made her one of the most important deities in times of conflict.
In addition to her wisdom and military prowess, Athena was a guardian of the city and its values. As the protector of Athens, she was deeply tied to the development of the city’s civic life and cultural heritage. Athena’s protective nature extended not only to warfare but also to the city’s institutions, laws, and its artistic and intellectual achievements. She was seen as a patroness of the polis (city-state), symbolizing the harmony between intellect, civic duty, and the defense of the community. The Parthenon, the grand temple dedicated to Athena in Athens, reflected her importance as a protector and a symbol of the city’s greatness.

Aegira, Achaia 369-330 BCE

Aetolian League 205-150 BCE

Aigeira, Achaia 360-330 BCE

Aigiale, Amorgos, Cyclades 3rd-2nd centuries BCE

Ainianes, Thessaly 3rd-2nd centuries BCE

Akanthos, Macedon 400-358 BCE

Akanthos, Macedon 400-358 BCE

Akanthos, Macedon 400-358 BCE

Akanthos, Macedon 400-358 BCE

Anaktorion, Akarnania 350-300 BCE

Andragoras 246-238 BCE

Antigonos II Gonatas 277-239 BCE

Antioch, Syria 312-281 BCE

Arabia 5th-3rd centuries BCE

Aretas II 129-104 BCE

Argos Amphilochikon, Akarnania 300-200 BCE

Ariarathes IV 220-163 BCE

Ariarathes IX Eusebes 88/7 BCE

Ariarathes V 134/3 BCE

Ariarathes VI Epiphanes 118/7 BCE

Ariarathes VII 104/3 BCE

Ariarathes X 42-36 BCE

Ariobarzanes I Philoromaios 83/2 BCE

Ariobarzanes II 63-52 BCE

Ariobarzanes III 52-42 BCE

Assos, Troas 350-300 BCE

Assos, Troas 400-241 BCE

Ataxerxes III Okhos 343-337 BCE

Athens 140-175 CE

Athens 454-404 BCE

Athens 454-404 BCE

Athens ca 150 Ce

Athens, Attica 130-90 BCE

Athens, Attica 130-90 BCE

Athens, Attica 166-57 BCE

Athens, Attica 224-198 BCE

Athens, Attica 264-267 CE

Athens, Attica 264-267 CE

Athens, Attica 264-267 CE

Athens, Attica 270-261 BCE

Athens, Attica 2nd-3rd Centuries CE

Athens, Attica 307-300 BCE

Athens, Attica 322/17-307 BCE

Athens, Attica 322-307 BCE

Athens, Attica 340-322 BCE

Athens, Attica 36-33 BCE

Athens, Attica 39-37 BCE

Athens, Attica 4th century BCE

Athens, Attica 87/6 BCE

Athens, Attica 99-98 BCE

Athens, Attica ca 120-150 CE

Audoleon 315-28 BCE

Azetium, Apulia 300-275 BCE

Balakros 333-323 BCE

Barata, Lykaonia 244-249 CE

Batis of Gaza 353-333 BCE

Belos, Syria mid-5th century BCE

Chares 350 BCE

Corinth 350-306 BCE

Demetrios I Poliorketes 290-283 BCE

Demetrios Poliorketes 306-283 BCE

Dorylaion, Phrygia 300-100 BCE

Echinos 345-300 BCE

Edom 4th century BCE

Elaia, Aeolis 340-330 BCE

Elaia, Aiolis 350-320 BCE

Eleutheria, Mysia 4th century BCE

Epeiros, The Athamanes 168-146 BCE

Eumenes I 255-241 BCE

Grimenothyrae, Phrygia

Hananiyah 375-333 BCE

Hephaistia, Lemnos 300 BCE

Hephaistia, Lemnos 386-261 BCE

Heraia, Peloponnese 370-350 BCE

Hipponion, Bruttium 3rd century BCE

Holmoi, Cilicia 375 BCE

Ilion, Troas 301-281 BCE

Itanos, Crete 320-280 BCE

Itanos, Crete 350-320 BCE

Kadoi, Phrygia 1st century BCE

Kibyra Minor, Cilicia 2nd-1st centuries BCE

Klazomenai, Ionia 4th century BCE

Koinon of Macedon 222-235 CE

Koinon of Macedon 222-235 CE

Koinon of Macedon 222-235 CE

Koinon of Macedon 222-235 CE

Koinon of Macedon 231-235 CE

Koinon of Macedon 238-244 CE

Koinon of Macedon 238-244 CE

Kolone, Troas 4th century BCE

Kolone, Troas 4th Century BCE
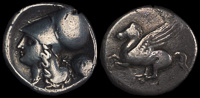
Koronta, Akarnania 300-250 BCE

Kyparissia, Messenia 193-211 CE

Lamia, Thessaly 325-300 BCE

Lampsakos, Mysia 350-250 BCE

Lebedo-Ptolemais, Ionia 375-350 BCE
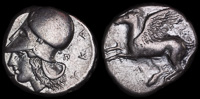
Leukas, Akarnania 375-350 BCE

Lokri Epizephyrii, Bruttium 360-268 BCE

Lokris Epiknemidia 338-300 BCE

Lokris Opuntii 325-300 BCE

Lokris Opuntii 351-338 BCE

Lysanias 40-36 BCE

Lysimachos 287-281 BCE

Mantineia, Arkadia 370-240 BCE

Mazakes 331-323 BCE

Medeon, Akarnanai 300-250 BCE

Megara, Megaris 198-209 CE

Methymna, Lesbos 350-240 BCE
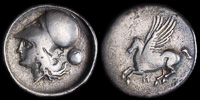
Metropolis, Akarnania 300-250 BCE

Mithradates I Kallinikos 96-70 BCE

Mothone 193-217 CE

Mothone, Messenia 198-217 CE

Myrina, Aeolis 400-200 BCE

Myrina, Aeolis 4th century BCE

Myrina, Aeolis 4th-3rd century BCE

Myrina, Lemnos 386-261 BCE

Myrleia, Bithynia 4th-3rd centuries BCE

Mysia, Parion 300-200 BCE

Naulochos 350-340 BCE

Neonteichos, Aeolis 300-100 BCE

Northern Arabia 4th-3rd centuries BCE

Olympus, Lycia 166-81 BCE

Orikos, Illyria 230-168 BCE

Orthe, Thessaly 4th-3rd cent BCE

Panormos, Sicily 275-212 BCE

Patrae, Achaia 177-192 CE

Patrai, Achaia 45-40 BCE

Pedasa, Ionia 4th century BCE

Peirasia, Thessaly 4th century BCE

Pella, Macedon 187-31 BCE

Pergamon 133-27 BCE

Pergamon 282-133 BCE

Pergamon 310-282 BCE

Pergamon, Mysia 310-282 BCE

Phaloria, Thessaly 302-286 BCE

Pharaonic Kingdom 5th-mid 4th Cen BCE

Pharsalos, Thessaly 4th-3rd cent BCE

Philetairos 282-263 BCE

Philip V 221-179 BCE

Philopator 20 BCE – 17 CE

Poseidion, Cilicia 4th century BCE

Potidaia, Macedon 380-350 BCE

Priene, Ionia 240-170 BCE

Priene, Ionia 300-140 BCE

Priene, Ionia 334-320 BCE

Pylos, Messenia 193-217 CE

Sabakes 340-333 BCE

Samothrace 280 BCE

Savatra, Lykaonia 138-161 CE

Seleukos I Nikator 296-281 BCE

Selge, Pisidia 350-300 BCE

Sestos, Thrace 400-350 BCE

Sigeion, Troas 355-334 BCE

Skotussa, Thessaly 3rd century BCE

Skythia, Olbia 120-110 BCE

Soloi, Cilicia 400-350 BCE

Sophytes 323-240 BCE

Tegea, Arkadia 4th-3rd cent BCE

Telos, Caria 350 BCE

Thessalonika, Macedon 187-31 BCE

Thessalonika, Macedon after 148 BCE

Thourion, Lukania 425-400 BCE

Thyrrheion, Akarnania 350-300 BCE

Tissaphernes 400-395 BCE

Trapezopolis, Caria 138-161 CE

Troizen, Argolis 330-300 BCE

Tyrrhenoi, Sicily 354-336 BCE

Yehud 375-332 BCE
